Interactive Learning for Point-Cloud Motion Segmentation
Published in Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 32, no. 7, pp. 51-60, 2013
Recommended citation: Yerry Sofer, Tal Hassner, and Andrei Sharf. Interactive Learning for Point-Cloud Motion Segmentation. Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 32, no. 7, pp. 51-60, 2013.
Abstract
Segmenting a moving foreground (fg) from its background (bg) is a fundamental step in many Machine Vision and Computer Graphics applications. Nevertheless, hardly any attempts have been made to tackle this problem in dynamic 3D scanned scenes. Scanned dynamic scenes are typically challenging due to noise and large missing parts. Here, we present a novel approach for motion segmentation in dynamic point-cloud scenes designed to cater to the unique properties of such data. Our key idea is to augment fg/bg classification with an active learning framework by refining the segmentation process in an adaptive manner. Our method initially classifies the scene points as either fg or bg in an un-supervised manner. This, by training discriminative RBF-SVM classifiers on automatically labeled, high-certainty fg/bg points. Next, we adaptively detect unreliable classification regions (i.e. where fg/bg separation is uncertain), locally add more training examples to better capture the motion in these areas, and re-train the classifiers to fine-tune the segmentation. This not only improves segmentation accuracy, but also allows our method to perform in a coarse-to-fine manner, thereby efficiently process high-density point-clouds. Additionally, we present a unique interactive paradigm for enhancing this learning process, by using a manual editing tool. The user explicitly edits the RBF-SVM decision borders in unreliable regions in order to refine and correct the classification. We provide extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments on both real (scanned) and synthetic dynamic scenes.
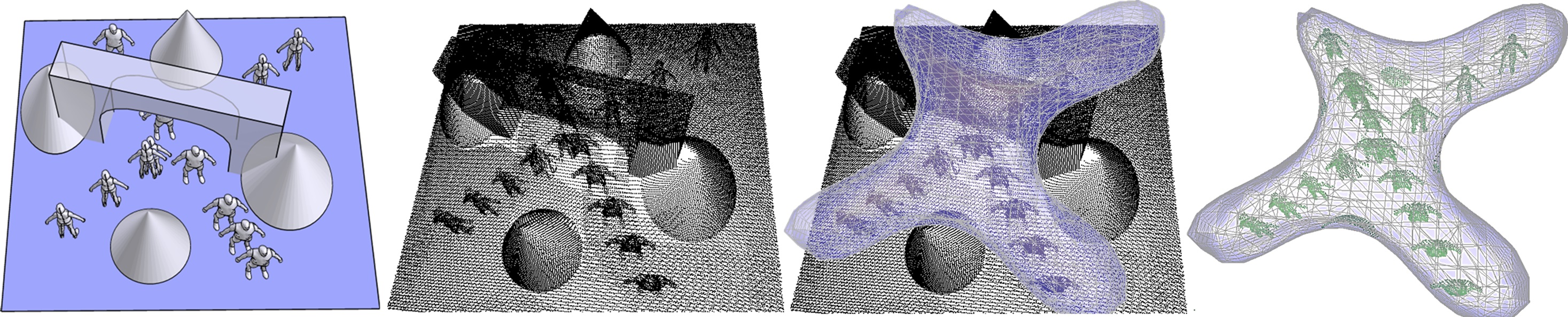
Motion segmentation of dynamic point-cloud scenes. Given a dynamic scene of two people walking under a bridge with their paths intersecting (left), we simulate its scan (mid-left) and compute its fg/bg segmentation. We adaptively refine the decision border of our classifier (mid-right) resulting in an accurate motion (fg) separation (right).
Dynamic point cloud data
We provide the data used in the experiments reported in our paper. The data in the files below is formatted one point per row. Each row includes the following values:
X Y Z nX nY nZ R G B
Where:
- X Y Z are the spatial coordinates of each point (float)
- nX nY nZ are the estimated normal at that point (float)
- R G B are the color values at the point, but should not be used / unreliable (integer)
Each archive contains one file per frame, where file names indicate the frame number. The following point clouds are available:
- Real scan - set2 (483Mb)
- Real scan - data2 (130Mb)
- Real scan - data3 (134Mb)
- Real scan - scan2 (106Mb)
- Synthetic scan - sc2_10 (3Mb)
- Synthetic scan - sc3_10 (4.5Mb)
- Synthetic scan - complex (12.5Mb)
This data is free to use for academic purposes only. If you use this data in your work, please provide appropriate citations to our paper.
